Insurance
Insurance is a type of contract between an individual or an organization (the policyholder) and an insurance company or insurer. The policyholder pays a premium to the insurer in exchange for protection against financial loss or damage due to specific events or risks, as defined in the policy. Insurance policies can cover a wide range of risks, such as property damage, liability, illness, disability, death, and many others. Depending on the type of insurance policy, the insurer may be responsible for reimbursing the policyholder for covered losses or providing other types of benefits or services, such as medical treatment or legal assistance
Overall, insurance is a crucial tool for managing risks and protecting against financial losses that could otherwise be devastating. It provides individuals and businesses with peace of mind and helps them to mitigate potential financial liabilities.
Changes
- Insurable interest
- Utmost good faith
- Proximate cause
- Indemnity
- Subrogation
Insurance planning adheres to a structured risk management process, which includes:
- Identify Risks: Recognize potential threats, such as accidents or property damage.
- Evaluate Risks: Assess likelihood and impact.
- Select Strategy: Choose to retain, transfer, reduce, or avoid each risk.
- Implement: Put chosen strategies in place, like buying insurance or safety measures.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review and update strategies for continued effectiveness.
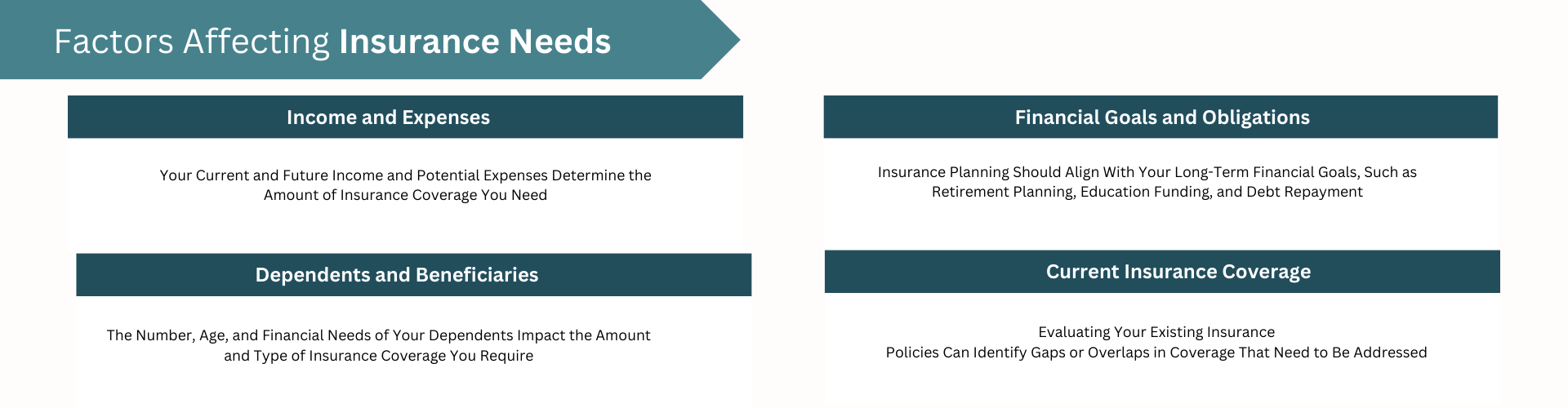
factors effecting insurance need:
Income and Expenses, Dependent and beneficiaries, Financial Goals and obligations, Existing Insurance Cover